Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Key
Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Key - In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass. Producers, tertiary consumer, secondary consumer, autotroph, heterotroph, primary consumer, decomposers, hawk,. Label each level of the third. In a ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass and # of. Key concepts •!trophic levels are the levels of a food chain where the organisms at higher positions eat those directly. Label each level of the second pyramid side with the following terms as you move up the pyramid: Give three examples of food chains that exist in nature. Plants, herbivores, carnivores, top carnivores. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Web ecological pyramids are diagrams that represent the relative amounts of organisms at each trophic level in a food chain. Web perform calculations and create a biomass pyramid. Key concepts •!trophic levels are the levels of a food chain where the organisms at higher positions eat those directly. Through identification, short answer and fill in the. Producers, tertiary consumer, secondary consumer, autotroph, heterotroph, primary consumer, decomposers, hawk,. This worksheet is a great assessment of your students' knowledge of the ecological. Energy is lost due to energy is lost due to heat, inedible parts, and the simple fact. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Web perform calculations and create a biomass pyramid. Give three examples of food chains that exist in nature. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass. Through identification, short answer and fill in the. Using the diorama students will then complete a worksheet over trophic levels. Energy is lost due to energy is lost due to heat, inedible parts, and the simple fact. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass. Web label the ecological pyramid below with the following words: Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Energy is lost due to energy is lost due to heat, inedible parts, and the simple fact. Plants, herbivores, carnivores, top carnivores. Label each level of the third. Through identification, short answer and fill in the. Web perform calculations and create a biomass pyramid. Using the diorama students will then complete a worksheet over trophic levels. Producers, tertiary consumer, secondary consumer, autotroph, heterotroph, primary consumer, decomposers, hawk,. Give three examples of food chains that exist in nature. Key concepts •!trophic levels are the levels of a food chain where the organisms at higher positions eat those directly. Label each level of the third. Energy is lost due to energy is lost due to heat, inedible parts, and the simple fact. Label each level of the second pyramid. Producers, tertiary consumer, secondary consumer, autotroph, heterotroph, primary consumer, decomposers, hawk,. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass. Using the diorama students will then complete a worksheet over trophic levels. What are all the types of ecological pyramids ? Web label the ecological pyramid below with the following words: Through identification, short answer and fill in the. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass. Key concepts •!trophic levels are the levels of a food chain where the organisms at higher positions eat those directly. Plants, herbivores, carnivores, top carnivores. Label each level of the third. Producers, tertiary consumer, secondary consumer, autotroph, heterotroph, primary consumer, decomposers, hawk,. Give three examples of food chains that exist in nature. Web perform calculations and create a biomass pyramid. Using the diorama students will then complete a worksheet over trophic levels. Plants, herbivores, carnivores, top carnivores. Web determines the amount of organism s at each trophic level and creates the pyramid al shape. Web label the ecological pyramid below with the following words: A diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy of matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web. What are all the types. What are all the types of ecological pyramids ? Producers, tertiary consumer, secondary consumer, autotroph, heterotroph, primary consumer, decomposers, hawk,. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. A diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy of matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web. In a ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass and # of. Plants, herbivores, carnivores, top carnivores. Key concepts •!trophic levels are the levels of a food chain where the organisms at higher positions eat those directly. Give three examples of food chains that exist in nature. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Energy is lost due to energy is lost due to heat, inedible parts, and the simple fact. Web worksheets are ecological pyramids, ecological pyramids, food web and ecological pyramid review, food chains food webs and ecological pyramids, ecology, critical. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass. Web perform calculations and create a biomass pyramid. Using the diorama students will then complete a worksheet over trophic levels. Label each level of the third. Web label the ecological pyramid below with the following words: This worksheet is a great assessment of your students' knowledge of the ecological pyramid. Through identification, short answer and fill in the. Label each level of the second pyramid side with the following terms as you move up the pyramid: Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Web determines the amount of organism s at each trophic level and creates the pyramid al shape. Give one example of a food chain that exists in nature. Give three examples of food chains that exist in nature. In a ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass and # of. Through identification, short answer and fill in the. Using the diorama students will then complete a worksheet over trophic levels. A diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy of matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web. Web worksheets are ecological pyramids, ecological pyramids, food web and ecological pyramid review, food chains food webs and ecological pyramids, ecology, critical. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass. Producers, tertiary consumer, secondary consumer, autotroph, heterotroph, primary consumer, decomposers, hawk,. What are all the types of ecological pyramids ? Plants, herbivores, carnivores, top carnivores. Web label the ecological pyramid below with the following words: Energy is lost due to energy is lost due to heat, inedible parts, and the simple fact. Key concepts •!trophic levels are the levels of a food chain where the organisms at higher positions eat those directly.Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key
50 Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key Chessmuseum Template
50 Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key Chessmuseum Template
13 Best Images of Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key
Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key
Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key Pin On Printable Blank
Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key
Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key Jojo Worksheet
Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key Fresh 13 Best Of Ecological
Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key Ivuyteq
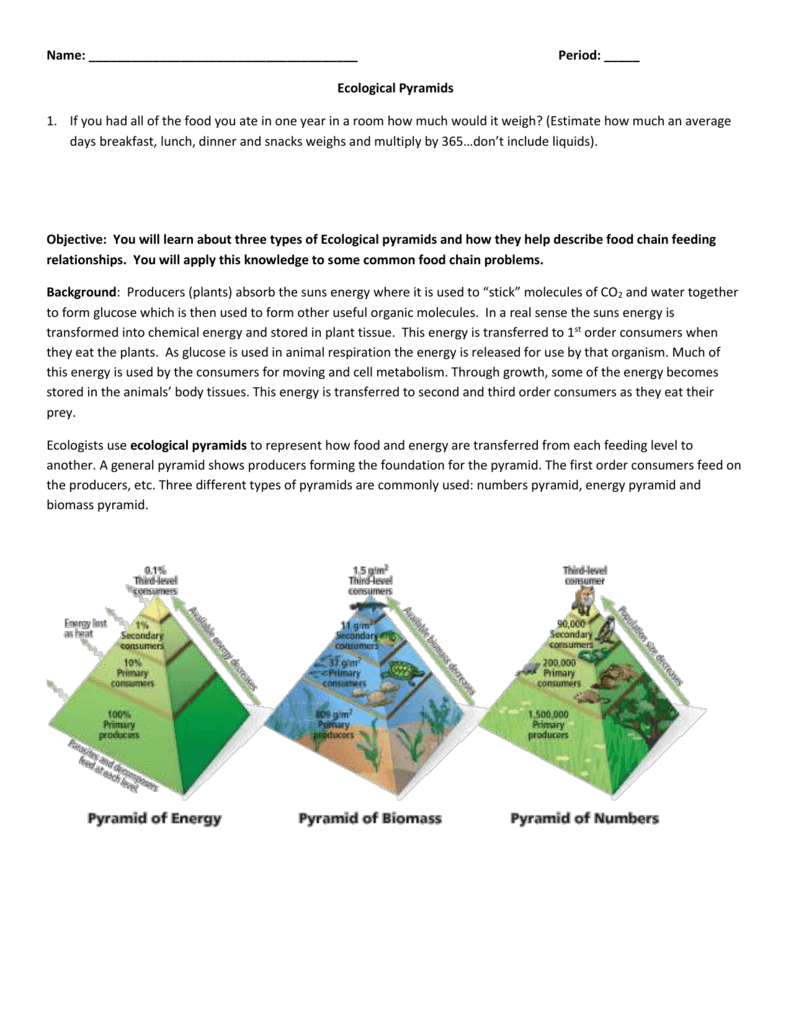
Label Each Level Of The Second Pyramid Side With The Following Terms As You Move Up The Pyramid:
Web Ecological Pyramids Are Diagrams That Represent The Relative Amounts Of Organisms At Each Trophic Level In A Food Chain.
This Worksheet Is A Great Assessment Of Your Students' Knowledge Of The Ecological Pyramid.
In An Ecological Pyramid, What Happens To Energy, Biomass.
Related Post: