Gas Laws Worksheet 2 Answer Key
Gas Laws Worksheet 2 Answer Key - N = pv = (2.8 atm)(98 l) = 11. Web the gas laws consist of three fundamental laws: Each quantity in the equation is usually expressed in the following units: P t = p 1 + p 2 + p 3 +. Dalton's law sates that the total pressure of a gas mixture is the. The correct answer is given in parentheses at the end of the. Charles’ law, boyle’s law, and avogadro’s law (all of which will later combine into the general gas equation and ideal. Web heating and cooling curves part 2 answer key; Chemistry name _ chapter 13: A brief introduction to the gas laws using the gas properties html5 phet simulation. Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. Atm = 760 mm hg = 101 kpa= 760.0 torr. P = pressure, measured in atmospheres. Web consider a sample of gas in a cylinder with a moveable piston. The correct answer is given in parentheses at the end of the. Web consider a sample of gas in a cylinder with a moveable piston. Dalton's law sates that the total pressure of a gas mixture is the. P = pressure, measured in atmospheres. Web therefore, we can assign a pressure to each gas in a mixture, called its partial pressure, pi. Web gas law worksheet #2 (dalton’s law and ideal gas. Calculate the ratio of effusion rates for nitrogen (n2) and neon (ne).υa= √mb = √20= 0.845 υb √ma. Web therefore, we can assign a pressure to each gas in a mixture, called its partial pressure, pi. P = pressure, measured in atmospheres. The correct answer is given in parentheses at the end of the. Charles’ law, boyle’s law, and avogadro’s. Solve each of the following problems. If 22 l of nitrogen at 748 mm hg are compressed to 725 mm hg at constant temperature. Each quantity in the equation is usually expressed in the following units: Each of these laws can be derived. Some of the worksheets for this concept are supplemental activities, guilford county schools home,. V = volume, measured in liters. Web gas law worksheet #2 (dalton’s law and ideal gas law) dalton’s law: 1 atm = 760.0 mm hg = 101.3 kpa. Determine the total pressure of a gas mixture that contains oxygen at a. Chemistry name _ chapter 13: The ideal gas law key directions: N = amount of gas,. Determine the total pressure of a gas mixture that contains oxygen at a. Each of these laws can be derived. Chemistry name _ chapter 13: Determine the total pressure of a gas mixture that contains oxygen at a. Charles’ law, boyle’s law, and avogadro’s law (all of which will later combine into the general gas equation and ideal. Solve each of the following problems. Assuming that no gas is lost or gained (constant n), what would happen to: Web therefore, we can assign a pressure. Chemistry name _ chapter 13: Each of these laws can be derived. Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. Atm = 760 mm hg = 101 kpa= 760.0 torr. Determine the total pressure of a gas mixture that contains oxygen at a. N = pv = (2.8 atm)(98 l) = 11. Each quantity in the equation is usually expressed in the following units: Web the gas laws consist of three fundamental laws: Gas laws ws ii date _/_/_ period _ this worksheet. P = pressure, measured in atmospheres. Web heating and cooling curves part 2 answer key; P t = p 1 + p 2 + p 3 +. If 22 l of nitrogen at 748 mm hg are compressed to 725 mm hg at constant temperature. Atm = 760 mm hg = 101 kpa= 760.0 torr. If 22.5 l of nitrogen at 748 mm hg are compressed. If 22 l of nitrogen at 748 mm hg are compressed to 725 mm hg at constant temperature. This first 5 activities can generally be completed in one class. N = pv = (2.8 atm)(98 l) = 11. The correct answer is given in parentheses at the end of the. Solve each of the following problems. Web gas law worksheet #2 (dalton’s law and ideal gas law) dalton’s law: Web the gas laws consist of three fundamental laws: The ideal gas law key directions: P t = p 1 + p 2 + p 3 +. Some of the worksheets for this concept are supplemental activities, guilford county schools home,. Gas laws ws ii date _/_/_ period _ this worksheet. Calculate the ratio of effusion rates for nitrogen (n2) and neon (ne).υa= √mb = √20= 0.845 υb √ma. Web heating and cooling curves part 2 answer key; V = volume, measured in liters. Assuming that no gas is lost or gained (constant n), what would happen to: Determine the total pressure of a gas mixture that contains oxygen at a. Each quantity in the equation is usually expressed in the following units: N = amount of gas,. Charles’ law, boyle’s law, and avogadro’s law (all of which will later combine into the general gas equation and ideal. Each of these laws can be derived. Web the gas laws consist of three fundamental laws: Assuming that no gas is lost or gained (constant n), what would happen to: Web therefore, we can assign a pressure to each gas in a mixture, called its partial pressure, pi. P = pressure, measured in atmospheres. N = pv = (2.8 atm)(98 l) = 11. Chemistry name _ chapter 13: Some of the worksheets for this concept are supplemental activities, guilford county schools home,. 1 atm = 760.0 mm hg = 101.3 kpa. Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. Web heating and cooling curves part 2 answer key; If 22.5 l of nitrogen at 748 mm hg are compressed to 725 mm hg at constant. The gas volume if the pressure is. Charles’ law, boyle’s law, and avogadro’s law (all of which will later combine into the general gas equation and ideal. Each of these laws can be derived. The ideal gas law key directions: P t = p 1 + p 2 + p 3 +.Behavior of Gases Worksheet for 9th 12th Grade Lesson
Ideal Gas Law Gizmo Answer Key Pdf What Are The 5 Gas Laws
Combined Gas Law Worksheet Answer Key —
Combined Gas Law Worksheet Answer Key —
Gas Laws Worksheet Answer Key
The Gas Laws Worksheet —
Gas Laws Worksheet 1 Answer Key —
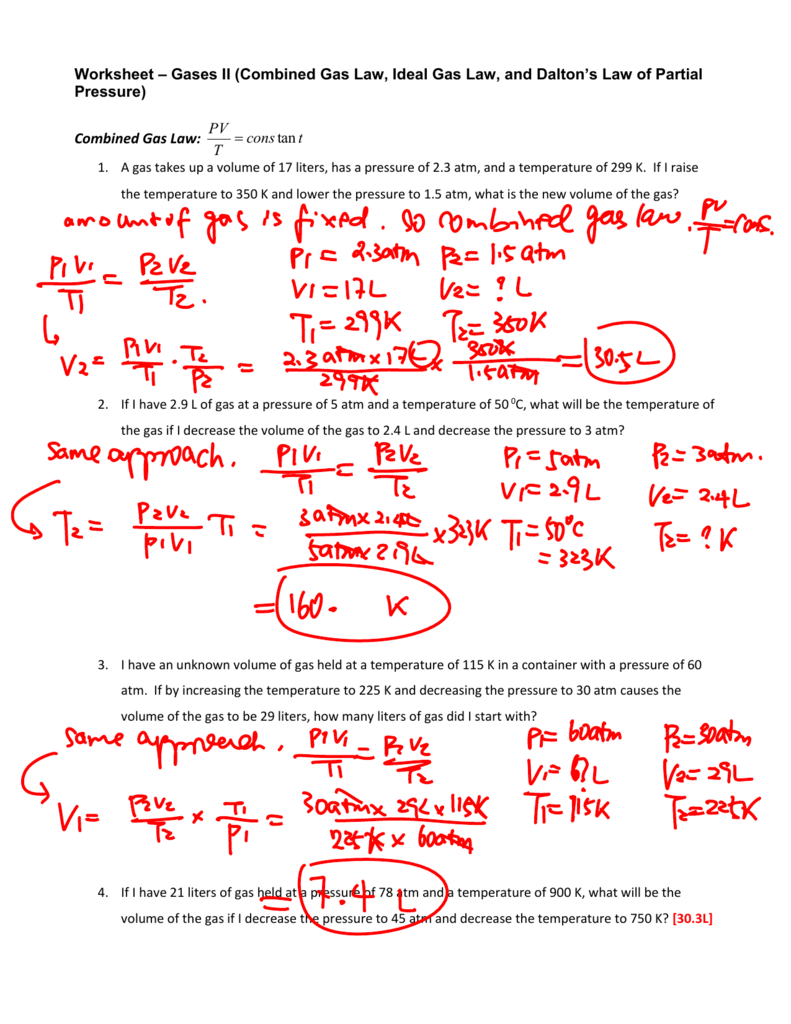
Worksheet Gas Laws II Answers
Gas Laws Practice Problems Worksheet Answers —
Gas Laws Worksheet 1 Answer Key —
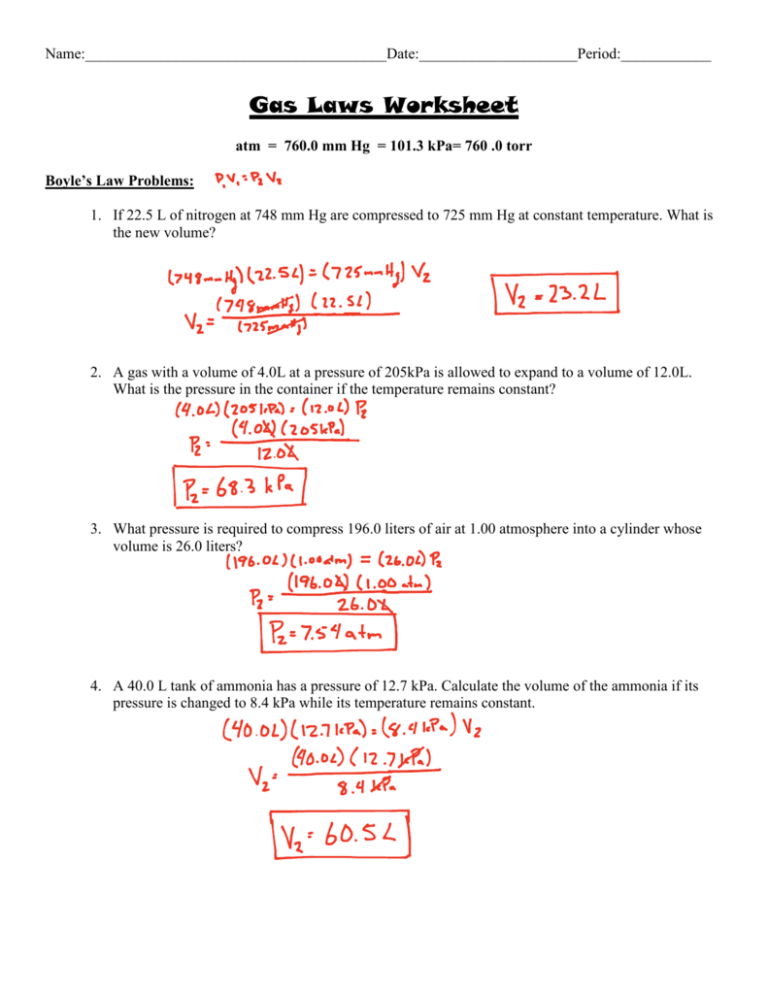
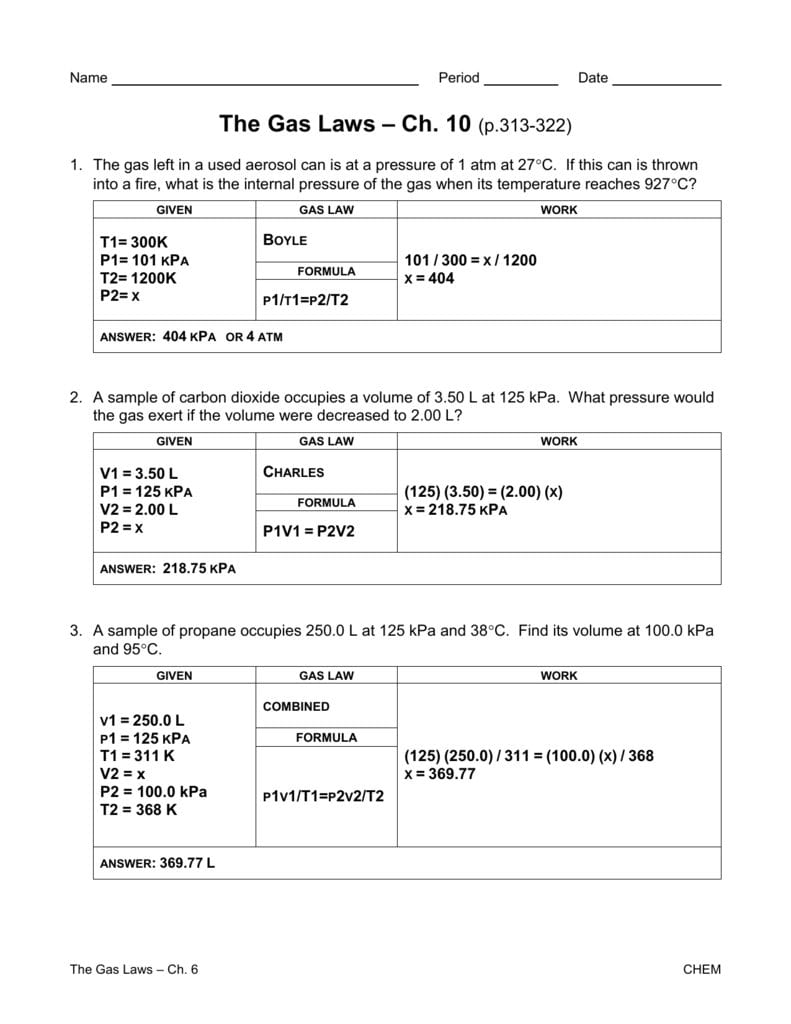
If 22 L Of Nitrogen At 748 Mm Hg Are Compressed To 725 Mm Hg At Constant Temperature.
V = Volume, Measured In Liters.
Calculate The Ratio Of Effusion Rates For Nitrogen (N2) And Neon (Ne).Υa= √Mb = √20= 0.845 Υb √Ma.
Web Gas Law Worksheet #2 (Dalton’s Law And Ideal Gas Law) Dalton’s Law:
Related Post: