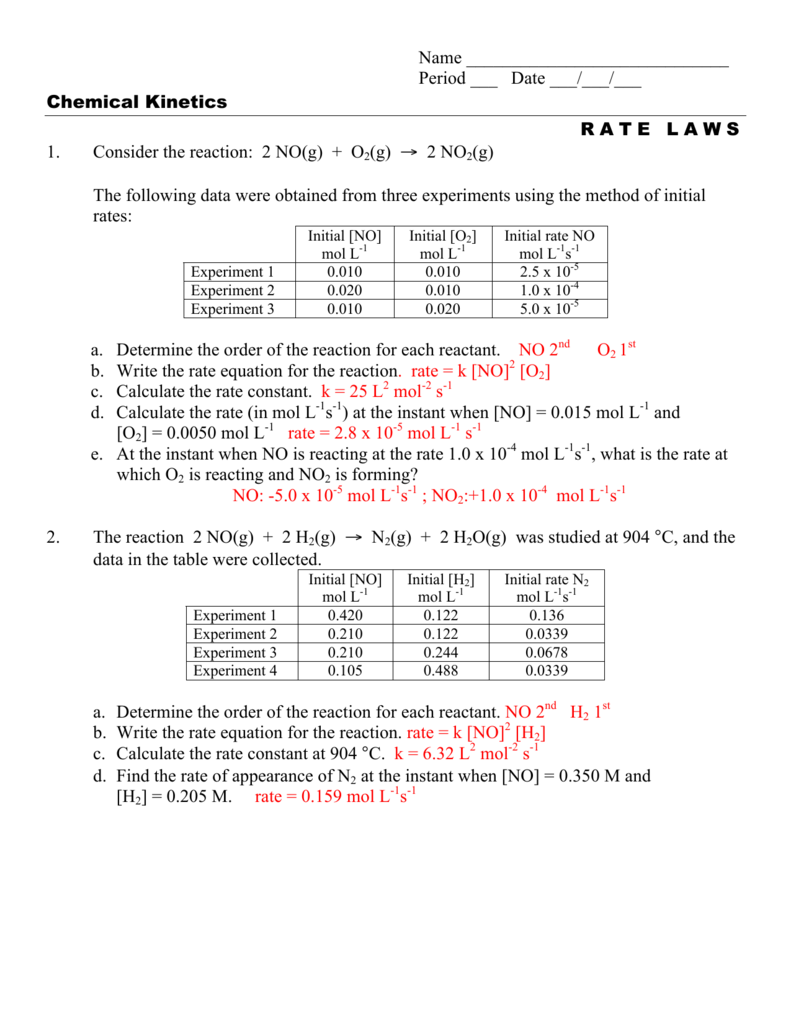
Rate Laws Worksheet Answers
Rate Laws Worksheet Answers - Web this quiz and worksheet will help gauge your understanding of rate constant and rate laws. Web a) rate is increased by a factor of 9 (nine times as fast as the original rate) b) rate is decreased to 1/9 the original rate 8. Web a) rate = k [no2]2 b) rate = k c) rate = k [h2] [br2]1/2 d) rate = k [no]2[o a) second order b) zero order c) 3/2 order d) third order 5. Write the rate law for the reaction. Web these math worksheets should be practiced regularly and are free to download in pdf formats. 100% (1 rating) transcribed image text: Web rate laws answer the following questions about rate laws. Use rate laws to calculate reaction rates. For the reaction 2 no (g) + cl2(g) → 2. Consider the following reaction between mercury (ii) chloride and the oxalate ion listed below. For the reaction 2 no (g) + cl2(g) → 2. Write the rate law for the reaction. 100% (1 rating) transcribed image text: Web rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions that describe the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction. The rate of a reaction is the change in concentration with respect. Web rate laws answer the following questions about rate laws. Consider the following reaction between mercury (ii) chloride and the oxalate ion listed below. Chem 1120 name integrated rate laws worksheet 2) the second order reaction: Web a) rate is increased by a factor of 9 (nine times as fast as the original rate) b) rate is decreased to 1/9. Consider the following reaction between mercury (ii) chloride and the oxalate ion listed below. Describe the difference between the rate constant and the rate of a reaction. Web these math worksheets should be practiced regularly and are free to download in pdf formats. Chem 1120 name integrated rate laws worksheet 2) the second order reaction: A plot of ln [. For the reaction 2 no (g) + cl2(g) → 2. Web determine the rate law for this reaction.•when concentration of a is doubled (exp. Explain the form and function of a rate law. 1 to 2), the initial rate doubleso•order with respect to a is 1when concentration of b is doubled. The reaction 2 no 2 (g) + o 3. Worksheet_answers (part 1) average rates, rate laws, method of initial rates, integrated rate laws answer the following questions: Describes the dependence of the (forward) rate on the concentrations of reactants. Use rate laws to calculate reaction rates. Consider the following reaction between mercury (ii) chloride and the oxalate ion listed below. Chem 1120 name integrated rate laws worksheet 2) the. Web rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions that describe the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction. Ln [ a] t = ( − k) ( t) + ln [ a] 0 y = m x + b. Topics to know for the quiz include reaction order and the rate law equation.. Web answer key rate law worksheet 1. Topics to know for the quiz include reaction order and the rate law equation. Explain the form and function of a rate law. Web a) rate = k [no2]2 b) rate = k c) rate = k [h2] [br2]1/2 d) rate = k [no]2[o a) second order b) zero order c) 3/2 order. The rate of a reaction is the change in concentration with respect to time of a product. Web determine the rate law for this reaction.•when concentration of a is doubled (exp. Web a) rate is increased by a factor of 9 (nine times as fast as the original rate) b) rate is decreased to 1/9 the original rate 8. Web. A plot of ln [ a] t versus t for. 100% (1 rating) transcribed image text: Web rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions that describe the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction. Ln [ a] t = ( − k) ( t) + ln [ a] 0 y = m x. Worksheet_answers (part 1) average rates, rate laws, method of initial rates, integrated rate laws answer the following questions: In the next example exercise, a linear format for the integrated rate law will be convenient: Use rate and concentration data to identify reaction. Write the rate law for the reaction. Web these math worksheets should be practiced regularly and are free. Web answer key rate law worksheet 1. The reaction 2 no 2 (g) + o 3 (g) → n 2 o 5 (s) +. Web determine the rate law for this reaction.•when concentration of a is doubled (exp. 1 to 2), the initial rate doubleso•order with respect to a is 1when concentration of b is doubled. Web this quiz and worksheet will help gauge your understanding of rate constant and rate laws. For the reaction 2 no (g) + cl2(g) → 2. Use rate and concentration data to identify reaction. Consider the following reaction between mercury (ii) chloride and the oxalate ion listed below. Web rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions that describe the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction. Web a) rate = k [no2]2 b) rate = k c) rate = k [h2] [br2]1/2 d) rate = k [no]2[o a) second order b) zero order c) 3/2 order d) third order 5. (and only for an elementary reaction) , the rate law can be. The rate of a reaction is the change in concentration with respect to time of a product. Describes the dependence of the (forward) rate on the concentrations of reactants. Worksheet_answers (part 1) average rates, rate laws, method of initial rates, integrated rate laws answer the following questions: Web rate laws answer the following questions about rate laws. Ln [ a] t = ( − k) ( t) + ln [ a] 0 y = m x + b. Calculate the rate constant, k. In the next example exercise, a linear format for the integrated rate law will be convenient: I (aq) +cio2 1o ci follows the rate. Explain the form and function of a rate law. The rate of a reaction is the change in concentration with respect to time of a product. Consider the following reaction between mercury (ii) chloride and the oxalate ion listed below. Describe the difference between the rate constant and the rate of a reaction. Web these math worksheets should be practiced regularly and are free to download in pdf formats. For the reaction 2 no (g) + cl2(g) → 2. Describes the dependence of the (forward) rate on the concentrations of reactants. Web answer key rate law worksheet 1. Use rate and concentration data to identify reaction. A plot of ln [ a] t versus t for. Ln [ a] t = ( − k) ( t) + ln [ a] 0 y = m x + b. Topics to know for the quiz include reaction order and the rate law equation. Write the rate law for the reaction. 100% (1 rating) transcribed image text: In the next example exercise, a linear format for the integrated rate law will be convenient: Web this quiz and worksheet will help gauge your understanding of rate constant and rate laws. Web rate laws (sometimes called differential rate laws) or rate equations are mathematical expressions that describe the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction.Gas Laws Worksheet Answer Key Gases Litre
Solve Ratio, Rates & Percent Problems worksheet
Pin on Printable Worksheet Template
Rate Law Worksheet 2
GTAwhfdqpryiz1
The answer says the rate law is rate=k[HNO2]^2 . And that is how we
Boyles And Charles Law Worksheet defendusinbattleblog Worksheet
Worksheet Rate Laws Differential Rate Laws 1 AP Chemistry 2020
More Gas Laws Worksheet Charles Law Worksheet Answer Key Chemistry
6 Best Images of Ratio Language Worksheets Rates and Ratios
I (Aq) +Cio2 1O Ci Follows The Rate.
Web Determine The Rate Law For This Reaction.•When Concentration Of A Is Doubled (Exp.
Web A) Rate = K [No2]2 B) Rate = K C) Rate = K [H2] [Br2]1/2 D) Rate = K [No]2[O A) Second Order B) Zero Order C) 3/2 Order D) Third Order 5.
Explain The Form And Function Of A Rate Law.
Related Post:





![The answer says the rate law is rate=k[HNO2]^2 . And that is how we](https://i.redd.it/75hcg6c0te6z.jpg)



