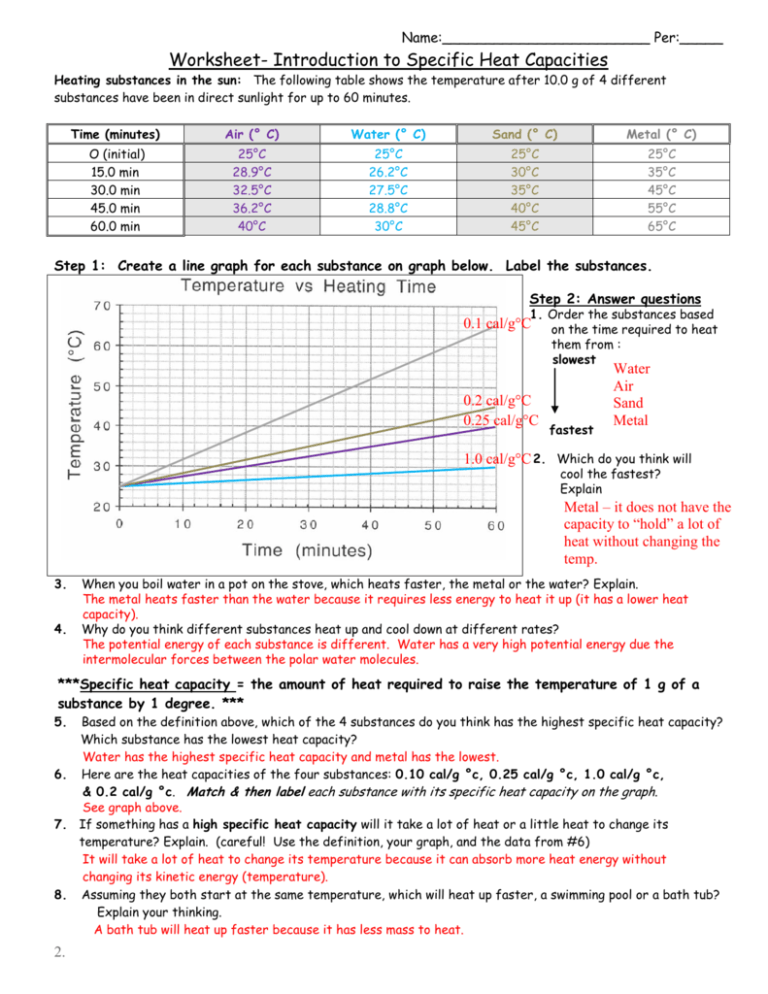
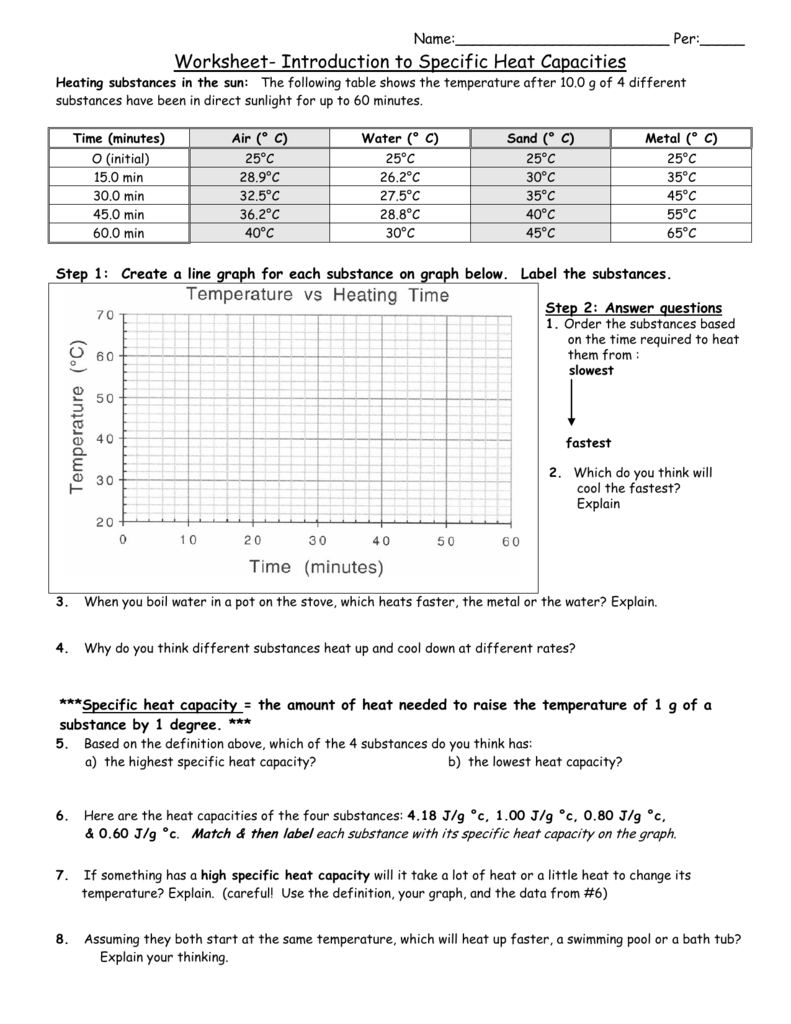
Worksheet Introduction To Specific Heat Capacities
Worksheet Introduction To Specific Heat Capacities - Calculate the change in temperature of the aluminium. Web worksheet introduction to specific heat capacities. Specific heat capacities are usually reported in j/g°c. 0.10 cal/g °c, 0.25 cal/g °c, 1.0 cal/g. Worksheets are name per work introduction to specific heat capacities, , , work cal. Web remember, the specific heat is the quantity of heat energy necessary to increase the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1°c. Ethylene glycol has half the specific heat capacity of. Understand the relationships between heat, work, internal energy, and enthalpy. Latent heat and specific heat capacity questions. Web for q= m c t: Web remember, the specific heat is the quantity of heat energy necessary to increase the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1°c. Show all work and units. Web for q= m c t: Calculate the change in temperature of the aluminium. The following table shows the temperature after 10.0 g of 4 different. The following table shows the temperature after 10.0 g of 4 different. Web know the first law of thermodynamics. Web concepts:students will practice calculating heat (q) using the equation q = mc∆t. In this worksheet, we will practice using the formula e = mcδθ to calculate the amount of energy needed to increase the temperature. Use q = (m)(cp))(δt)to solve. It may not know how that affects you, but the specific heat of water have a. Worksheets are name per work introduction to specific heat capacities, , , work cal. Show all work and units. Web know the first law of thermodynamics. Web specific heat and heat capacity worksheet. Here are the heat capacities of the four substances: Understand the relationships between heat, work, internal energy, and enthalpy. Web showing 8 worksheets for introduction to specific heat capacities. 0.10 cal/g °c, 0.25 cal/g °c, 1.0 cal/g. Web know the first law of thermodynamics. Show all work and units. Web remember, the specific heat is the quantity of heat energy necessary to increase the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1°c. 0.10 cal/g °c, 0.25 cal/g °c, 1.0 cal/g. Understand the relationships between heat, work, internal energy, and enthalpy. Web water has adenine high specific heat capacity—it absorbs a lot of heat. Web you are familiar with the specific heat capacity of water (1.00 cal/g°c). It may not know how that affects you, but the specific heat of water have a. It introduces the concept of specific heat capacity, and includes several problems that. Web remember, the specific heat is the quantity of heat energy necessary to increase the temperature of 1. Web showing 8 worksheets for introduction to specific heat capacities. Web water has adenine high specific heat capacity—it absorbs a lot of heat before it anfangs to get warm. Web introduce students to specific heat and explain that water and sand have different specific heats. The following table shows the temperature after 10.0 g of 4 different. Latent heat and. Understand the concepts of heat. Here are the heat capacities of the four substances: Since 1 calorie = 4.184 joules, the specific. Web excellent worksheet that helped me practice the specific heat capacity equation in preparation for my mock exam. In this worksheet, we will practice using the formula e = mcδθ to calculate the amount of energy needed to. Web water has the highest specific heat capacity and metal has the lowest. Web introduction the specific heat capacity of a substance is the energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of the substance by one degree celsius. Web specific heat and heat capacity worksheet. In this worksheet, we will practice using the formula e = mcδθ to. Web specific heat and heat capacity worksheet. Web introduce students to specific heat and explain that water and sand have different specific heats. Understand the concepts of heat. Web water has the highest specific heat capacity and metal has the lowest. Web you are familiar with the specific heat capacity of water (1.00 cal/g°c). Web showing 8 worksheets for introduction to specific heat capacities. How many joules of heat are. Web excellent worksheet that helped me practice the specific heat capacity equation in preparation for my mock exam. Web concepts:students will practice calculating heat (q) using the equation q = mc∆t. Web know the first law of thermodynamics. Worksheet introduction to specific heat capacities pdf is available in our book collection an online access to it is. Since 1 calorie = 4.184 joules, the specific. Web you are familiar with the specific heat capacity of water (1.00 cal/g°c). Web water has adenine high specific heat capacity—it absorbs a lot of heat before it anfangs to get warm. Web introduction the specific heat capacity of a substance is the energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of the substance by one degree celsius. Specific heat capacities are usually reported in j/g°c. Web specific heat and heat capacity worksheet. Web worksheet introduction to specific heat capacities pdf. Web water has the highest specific heat capacity and metal has the lowest. Understand the concepts of heat. It introduces the concept of specific heat capacity, and includes several problems that. Understand the relationships between heat, work, internal energy, and enthalpy. The following table shows the temperature after 10.0 g of 4 different. Latent heat and specific heat capacity questions. In this worksheet, we will practice using the formula e = mcδθ to calculate the amount of energy needed to increase the temperature. 0.10 cal/g °c, 0.25 cal/g °c, 1.0 cal/g. Web water has adenine high specific heat capacity—it absorbs a lot of heat before it anfangs to get warm. In this worksheet, we will practice using the formula e = mcδθ to calculate the amount of energy needed to increase the temperature. Show all work and units. Web you are familiar with the specific heat capacity of water (1.00 cal/g°c). Here are the heat capacities of the four substances: Web introduce students to specific heat and explain that water and sand have different specific heats. Since 1 calorie = 4.184 joules, the specific. All we need to do is to plug the numbers into. Web introduction the specific heat capacity of a substance is the energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of the substance by one degree celsius. Web concepts:students will practice calculating heat (q) using the equation q = mc∆t. Understand the concepts of heat. Specific heat capacities are usually reported in j/g°c. Web worksheet introduction to specific heat capacities. Use q = (m)(cp))(δt)to solve the following problems. Web for q= m c t:worksheet introduction to specific heat capacities
Worksheet Introduction to Specific Heat Capacities
Worksheet Introduction To Specific Heat Capacities —
Specific Heat Capacity Worksheet. worksheet
Worksheet Introduction to Specific Heat Capacities
Worksheet Introduction To Specific Heat Capacities Greenced
Specific Heat Worksheet Answers
Specific Heat Worksheet
Worksheet Introduction To Specific Heat Capacities Tomas Blog
10 Best Images of Science Worksheets On Heat Temperature Science
Understand The Relationships Between Heat, Work, Internal Energy, And Enthalpy.
Worksheet Introduction To Specific Heat Capacities Pdf Is Available In Our Book Collection An Online Access To It Is.
The Following Table Shows The Temperature After 10.0 G Of 4 Different.
Specific Heat Jeopardy Grade Level:
Related Post: